MySQL Constraints
Constraint controls and maintains the integrity of information stored in the database. It is basically a column or attribute or a combination of attribute to identify records of the database table.
These are the MySQL Constraints -
Primary Constraint
Primary Constraint of a relational table, uniquely identifies each record in the table. In some tables, combination of more than on attributes is declared as primary key.
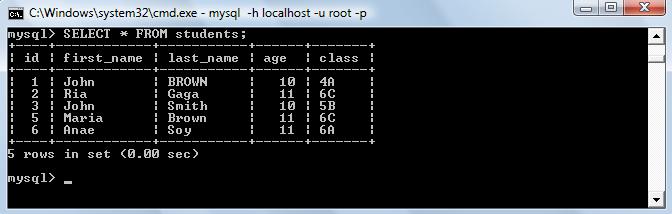
In the above students, id column is the primary key.
Foreign Constraint
Foreign Constraint is a non-key attribute whose value is derived from the primary key of another table. The relationship between two tables is established with the help of foreign key.
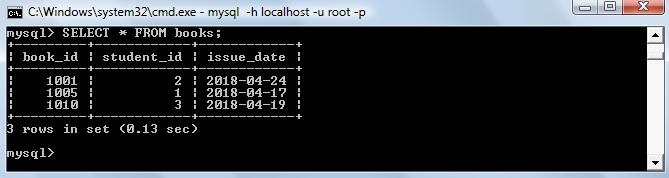
In the above books table, student_id is a foreign key.
NOT NULL Constraint
NOT NULL constraint permits that a column can not contain any NULL value. If you want to have a column not NULL value, then define that column NOT NULL constraint.
mysql->CREATE TABLE STUDENTS (id INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, first_name NOT NULL VARCHAR(20),
last_name NOT NULL VARCHAR(20), age INT(11), class NOT NULL VARCHAR(10), PRIMARY KEY(id));

In the above statement, all fields define NOT NULL constraint.
UNIQUE Constraint
UNIQUE Constraint uniquely identifies each record. It does not allow to insert a duplicate value in a column.
mysql->CREATE TABLE subject (id INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, sub_code VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
sub_name VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL, UNIQUE(id));
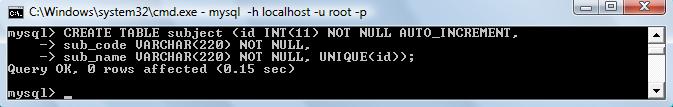
In the above statement, id column is defined as UNIQUE constraint.















